2. Perimeter Layer - Assess
Environment Setup
Look up the Stack Outputs
-
Go to the stack outputs and look for the website URL stored in the albEndpoint output value. Test access to the site by right clicking and opening in a new tab. Note the URL for your site as this will be used throughout this workshop.
-
While in the stack outputs, note the UniqueId value. This Id value will be used to identify the posture of your site within the automated scanner and the associated dashboard.
-
While still in stack outputs, right click the link in RedTeamHostSession and open in a new tab. This will launch an AWS Systems Manager Session Manager to the host you will use to perform manual scans against your site URL.
Website Scanning Environment and Tools
In order to test your AWS WAF ruleset, this lab has been configured with two scanning capabilities; a Red Team Host where you can invoke manual scanning and an automated scanner which runs from outside your lab environment.
The scanner performs 10 basic tests designed to help simulate and mitigate common web attack vectors.
- Canary GET - Should not be blocked
- Canary POST - Should not be blocked
- SQL Injection (SQLi) in Query String
- SQL Injection (SQLi) in Cookie
- Cross Site Scripting (XSS) in Query String
- Cross Site Scripting (XSS) in Body
- Inclusion in Modules
- Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) Token Missing
- Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) Token Invalid
- Path Traversal
These basic tests are designed to provide common examples you can use to test AWS WAF functionality. You should perform thorough analysis and testing when implementing rules into your production environments.
Website Scanning Environment and Tools - Manual Scanning
Once you have started a Session Manager connection to your Red Team Host, the scanner script can be invoked by typing the following command:
runscanner
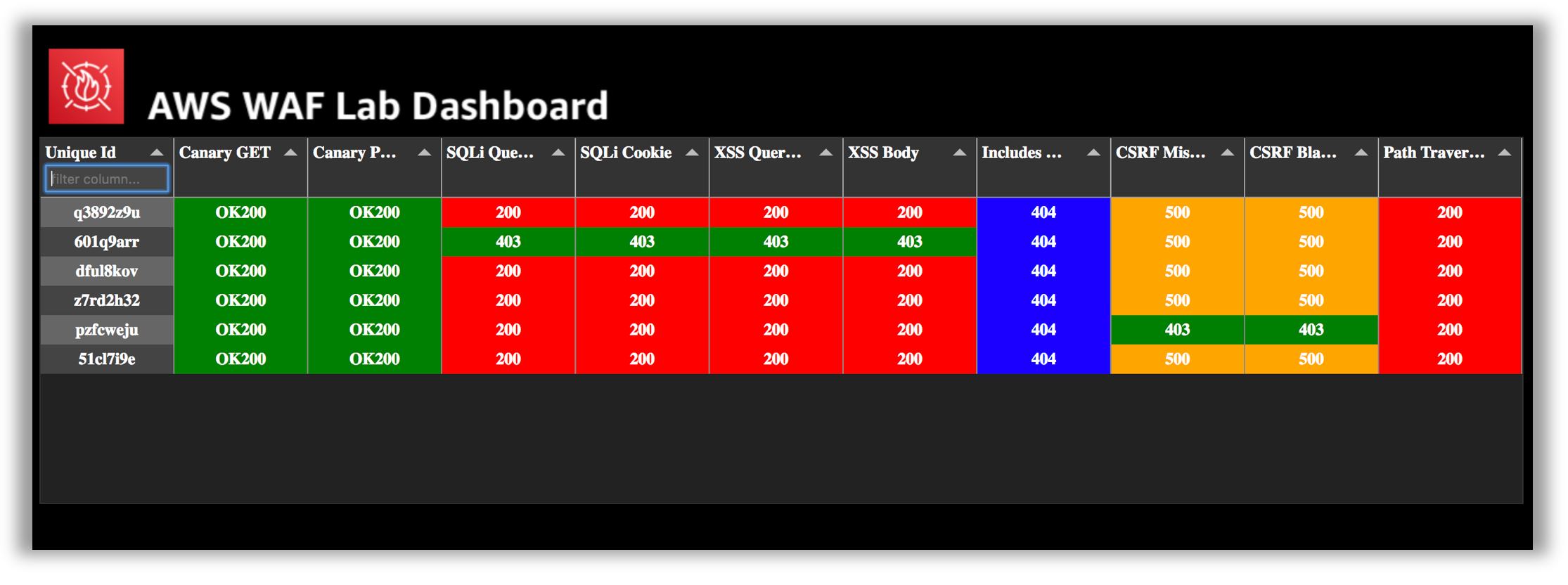
The scanner script will run each of the tests above and report back the following information:
- Request: The HTTP request command used.
- Test Name: The name of the test from list above.
- Result: The HTTP status code returned.
The logic in the scanner script color codes the response as follows:
- Green: 403 - Forbidden (Except for canary GET and POST tests.)
- Red: 200 - OK
- Blue: 404 - Not Found
- Yellow: 500 - Internal Server Error
About Scanner Tests and Colors: The color coding of the tests is provided to help to quickly assess the behavior of your WAF rules against their intended behavior. The goal is to achieve green color responses for all the tests. The purpose of the canary GET and POST requests are to ensure you have not unintentionally blocked legitimate traffic to your test site. These two tests should always return a 200 - OK response.
What are the results of running the scanner script? Were the simulated malicious requests blocked? As you can see by running the script there are several vulnerabilities that need to be addressed. In the remediate phase you will configure an AWS WAF Web ACL to block these requests. When AWS WAF blocks a web request based on the conditions that you specify, it returns HTTP status code 403 (Forbidden). For a full view of the request and response information, you can paste the Request command directly into the console and add the –debug argument.
The scanner script uses an open source HTTP client called httpie (https://httpie.org/). HTTPie—aitch-tee-tee-pie—is a command line HTTP client with an intuitive UI, JSON support, syntax highlighting, wget-like downloads, plugins, and more.
Website Scanning Environment and Tools - Automated Scanning
In addition to the manual scanning, automated scanning is also performed against your lab website. The automated tests are similar to the manual tests but the results are posted to a centralized scanning results dashboard along with the other workshop participants. You can identify the scanning results for your site using the UniqueId found in the CloudFormation outputs.
You can now proceed to the Remediate Phase.
Stuck? Watch this
This video has no audio